10K+ Global Brands That Trust Us!
Talk to an Expert

Expertise in DUE DILIGENCE
(5)
Enquiry Form
Among Asia Top 100
Consulting Firm

Get Consultation
Lowest Fees
1000 + Clients.

Overview of Due Diligence
Due diligence is an inspection and risk assessment of an upcoming business transaction basically; it is a background check to make sure that the parties to the transaction have the required information they need, to proceed with the transaction. A proper due diligence is required to reveal misrepresentation and fraudulent dealings in a major business transaction.
Due Diligence is the process by which confidential, legal, or financial and other material information are exchanges, reviewed and appraised by the interest parties who are going to enter into a Business transaction. Due diligence often refers to the in-depth research and study being done before signing an agreement or a business with a party.
Objective of Due Diligence
The objective of due diligence is to identify problems within the business, particularly those matters which may give rise to unexpected liabilities in the future. The main objectives of conducting Due Diligence are-
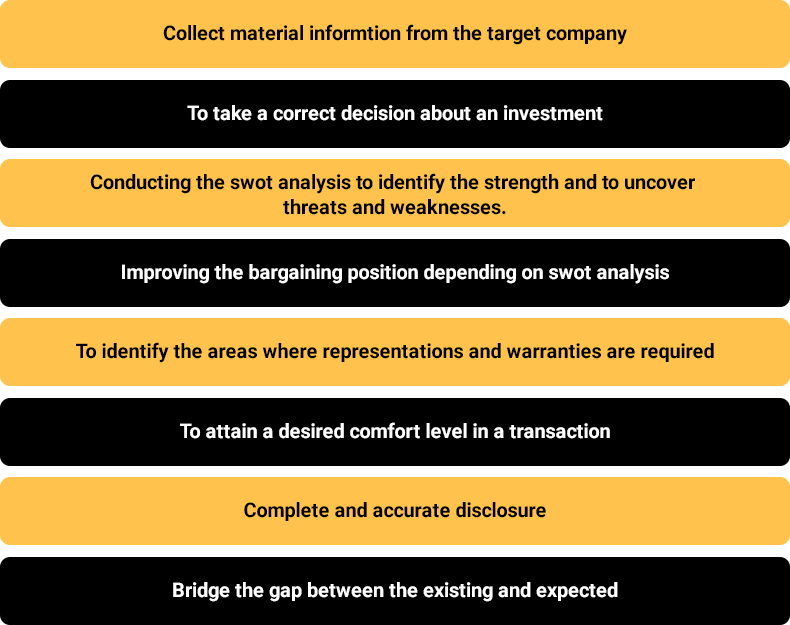
When Due Diligence is required?
Mergers and Acquisitions:
Due diligence is done from the perspective of the seller, as well as the buyer. While the consumer looks into the financials, litigation, patents, and a whole range of relevant information, the seller concentrates on the experience of the buyer, the financial abilities to complete the transaction, and the ability to fulfil responsibilities taken.
Partnership:
Due diligence is done for necessary alliances, necessary connections, business combinations, and such other alliances.
Joint Enterprise and Collaborations:
When one company joins hands with another, the reliability of the company is a subject of concern. Assuming the other company's stand includes the adequacy of supplies at their end.
Other than that, there are certain transactions that requires proper Due Diligence-
Types of Due Diligence
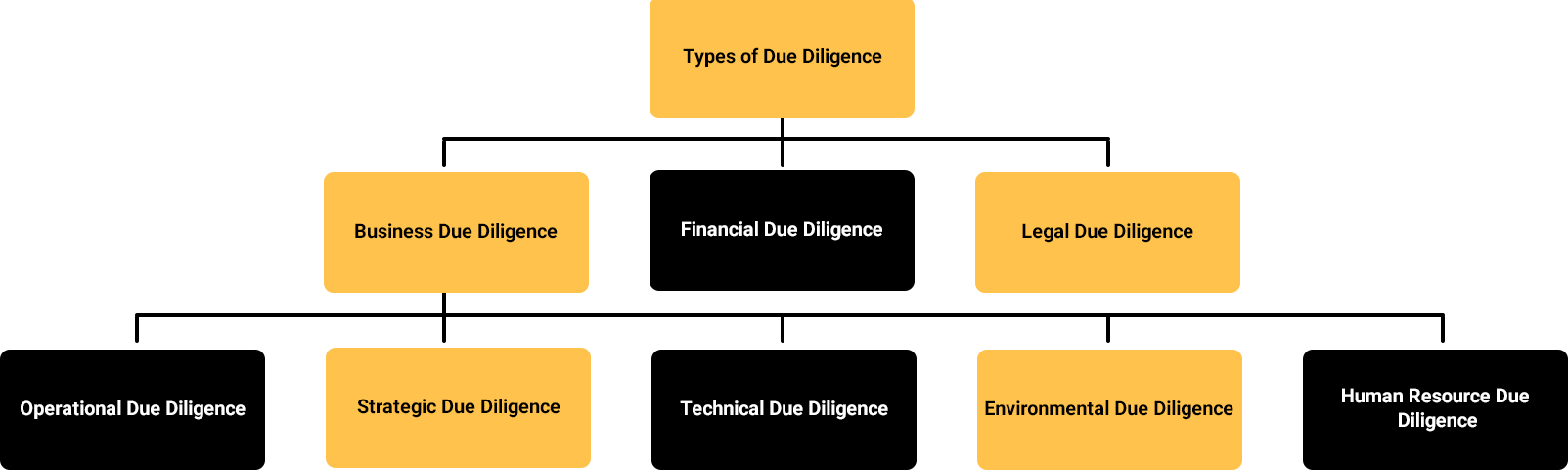
Due Diligence – Focused Area
Below mentioned are the key factors to be kept in mind while conducting Due Diligence-
Benefits of Due Diligence
Due diligence is needed so that the entity is well conscious of all the essential items like:-
Administration and Ownership
Analysis of who runs the Company
Capitalization
Examining how large and volatile is the Company and market. A contrastive analysis of both of them is needed.
Business Competitors and Industries
Research and compare the boundaries of competitors for a better comprehension of the target Company
Balance Sheet Review
This helps in interpreting the debt-to-equity ratio.
Revenue, Profit and Margin Bearings
To examine if there are any recent trends in the figures which may be rising, falling or stable?
Risks
It enables to learn industry-wide and Company-specific dangers, and all the checking if there are any on-going risks and trying to predict any futuristic unforeseeable threats in the future.
Capital History/Options and Probabilities
How long has the Company been dealing? For a short- term or long-term? Has there been a steady stock price?
Expectations
To maximize the profit for the future.
Documents required for Processing Due-Diligence
During Due-Diligence Process, the following types of Documents are required to be checked-
Procedure Involved in the Due Diligence Process
There are 3 stages in the Due diligence process-

I. Pre-Diligence Process
Pre-Diligence Process is the initial step for Due diligence process and is primarily the activity of management of paper works and people.
Differences between Due Diligence and Statutory Audit
In India, companies statutorily required to get their accounts audited by an unconventional Chartered Accountant. In some cases, companies needed to carry out an internal audit relating to their method. Due diligence is quite distinct from statutory audits. The difference between Due Diligence and Statutory Audit is given below:-
S.No | Statutory Audit | Due Diligence |
1. | Limited to Financial Analysis
| It not only includes the financial analysis but also includes Business plan, sustainability of business, future aspects, corporate and management prospects, legal issues, etc. |
2. | Based on Historical Data | Covers future growth prospects in addition to the historical data. |
3. | Statutory Audit is Mandatory. | Due Diligence is mandatory based on the transaction. |
4. | Provides Positive Assurance | Negative Assurance |
5. | Post-Mortem Analysis | Required for Future Decisions |
6. | Statutory Audit is always Uniform | Due Diligence varies according to the nature of transaction |
7. | The audit is recurring event | Occasional Event |
Tax Outline: Perspective on Due Diligence
Tax due diligence represents a prominent role in M&A determination; however the tax usually is not the primary concern in the context of M&A deals. Customarily, tax due diligence is carried out to explain more about the tax profile of the target and to reveal and quantify any tax exposures. Nevertheless, tax due diligence also comprises recognizing any tax upsides which may be accessible to the goal. It also supports in distinguishing and developing an appropriate procurement structure for the deal in question. The buyer needs to consider while negotiating for the tax protection to ensure that it does not affect the commerciality of the business for the seller. A tax due diligence is traditionally taken out to:
Fastzeal Support
FastZeal Conducts Inquiries, Data Rooms, and Searches for Due Diligence Surveys. We help our clients in preparing the questionnaire, Conducting Interviews with Beneficiary Management, Preparing Internal and External Public Registers. We provide various services related to Due-Diligence.
Questionnaire
Interviews with Beneficiary Management
Even as the administration is always best placed to present this information on the target's enterprise and prospects, we likewise will be handling management interviews, as we see this as an indispensable part of our 'due diligence' process.
Internal and External Public Registers
Public records may, though, not be entirely up to date, and this will form part of our crosschecking structure everywhere the due diligence inquiries. External explorations are not confined to:-
Why Fastzeal?
Because We Consist Of
Frequently Asked Questions:
The Whys are as follows
1. Evaluation and structuring of the transaction
2. Confirm/verify representations and warranties
3. Validate Business Plan
4. Transaction Management
1. Business Due Diligence:
2. Legal Due Diligence
3. Financial Due Diligence:
4. People Due Diligence
5. Environmental Due Diligence
6. Due Diligence Advisory
The Pillars are Decisive Rationale, Risk Reduction, and Post-Diligence
The Benefits of Due Diligence are as Follows.
1. Determine Administration and Ownership
2. Determine Capitalization
3. Analyse Business Competitors and Industries
4. Balance Sheet Review
5. Revenue, Profit and Margin Bearings
6. Risks Managements
7. Expectations Review
8. Capital history/options and Probabilities
1. Analyze the Capitalization
2. Resources Acquisition, and Margin
3. Rivals measurement
4. Comparative Study
5. Valuation Multiples
6. Administration and Share Ownership
7. Balance Sheet
8. History of Stock Costing
9. Stock Suspension
10. Expectations
11. Examine Long and Short-term Risks
It is a standard manner to use a 'virtual data' room addressing the issue of confidentiality. Nevertheless, you can reserve the right to demand as per need.
Public records may, though, not be entirely up to date, and this will form part of our crosschecking structure everywhere the due diligence inquiries.
In India, companies statutorily required to get their accounts audited by an unconventional Chartered Accountant. In some cases, companies needed to carry out an interior audit relating to their method. Due diligence is quite distinct from internal and statutory audits.
1. Identification and mitigation of risks in light of market practice and legal requirements
2. Changes in the structure of the transaction
3. Price adjustment
4. Conditions precedent
5. Representations and warranties
6. Verification of disclosures
7. Retention of the purchase price
8. Indemnity
9. Conditions after closing the deal.
The emphasis of due diligence into areas of human resources should be on:
1. Compliance with employment laws;
2. Employee contracts;
3. Employment-related liabilities (such as redundancy payments and social taxes);
4. Other issues are likely to be outlined in a due diligence checklist.



 Rated 4.9 By 10,000+ Customers.
Rated 4.9 By 10,000+ Customers.










































